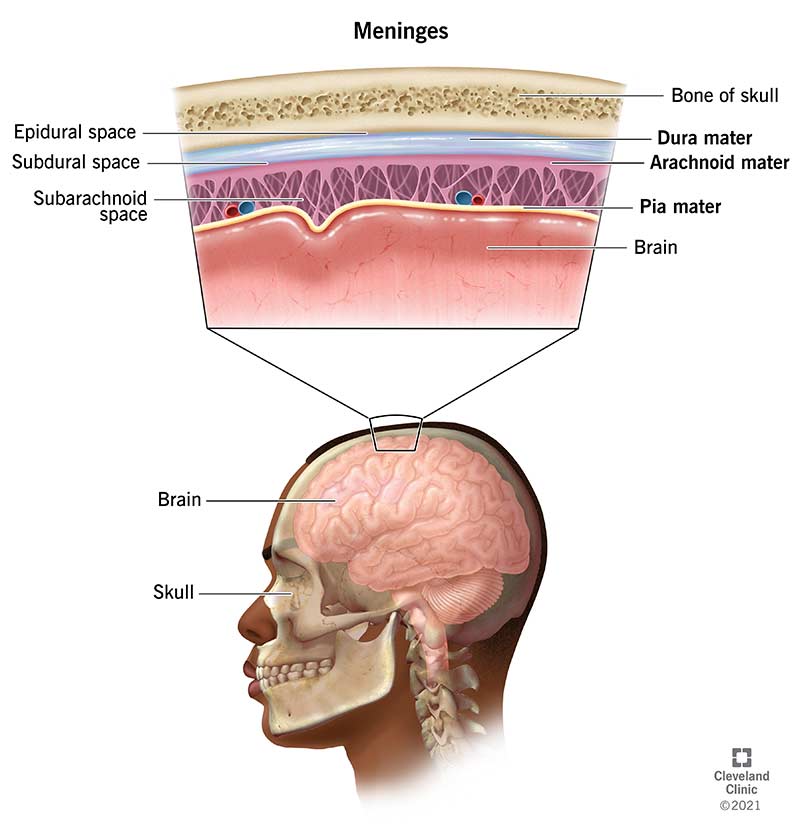
Character | Duramater | Arachnoid mater | Pia mater | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Etmology | Dura -> Hard mother | Arachnoid -> Cobweb like | Pia -> Soft mother | ||||||||||||||||||||
Layers | ▢ Endosteal layer: - Cranial venous sinuses are present between these two layers ▢ Meningeal layer: ❖ Folds:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
Location | Just beneath the skull | Below the Duramater | Below the Arachnoid mater, covering the brain | ||||||||||||||||||||
Spaces | ▢ Epidural space: Space just above the duramater (Between Skull and Duramater) ▢ Subdural space: Space below the duramater (Between duramater and arachnoid mater) | ▢ Subarachnoid space:
| No spaces |