
[MOE 2052]
[IOM 2003]
1 | Phasmid: - | Phasmid: + |
|---|---|---|
2 | Tail: Non-glandular | Tail: Glandular |
3 | Examples
| Examples
|
[IOM 1997]
[IOM 1998]
[IE 2003]
[BPKIHS -2015]
S.N. | Male Ascaris | Female Ascaris |
|---|---|---|
1 | Smaller | Bigger |
2 | Curved tail | Straight tail |
3 | Cloacal aperture present | Cloacal aperture absent; anus present |
4 | Pineal setae present in cloacal aperture | Absent |
5 | 55 pairs of anal papillae (50 pre-anal, 5 post-anal) | Absent |
6 | 55 pairs of cloacal apertures (50 pre-cloacal, 5 post-cloacal) | Absent |
7 | 3 apertures | 4 apertures |
S.N. | Medial Dorsal Lip | Ventrolateral Lips |
|---|---|---|
1 | 2 labial papillae (Tangoreceptor) | 1 in each lip |
2 | Absent | 1 simple lateral papilla (Chemoreceptor) in each |
3 | Amphid absent | Amphid (Chemoreceptor/Olfactoreceptor) in each |
[IOM-2013]
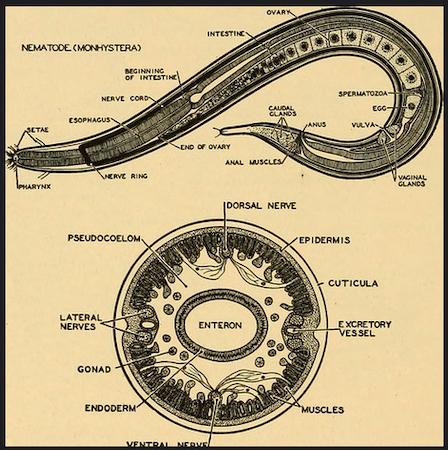
[IOM 2003]
[IOM 1998]
[IOM 1996]
Moulting | Location | Larval Stage |
|---|---|---|
1st moulting | Soil | 2nd instar / Infective rhabditiform larva |
2nd moulting | Lungs | 3rd instar larva |
3rd moulting | Lungs | 4th instar larva |
4th moulting | Small intestine | Adult (Sexually mature) |
[IOM 1997]
[BPKIHS-2013]
Moulting | Place | Larval Stage (Filariform) |
|---|---|---|
1st moulting | Soil | 2nd stage Filariform larva |
2nd moulting | Soil | 3rd stage Filariform larva (Infective stage) |
3rd moulting | Oesophagus | 4th stage Filariform larva |
4th moulting | Small intestine | Adult |
S.N. | Male Hookworm | Female Hookworm |
|---|---|---|
1 | Copulatory bursa with bursal rays present | Absent |
2 | Cloaca | Anus |
[IOM-2013]
[IOM 1997]
[BPKIHS 2004]
[MOE 2063]
[IOM 2003]
[IOM 1998]
[IOM 1997]
[IOM 1997]
[IOM 1997]
[IOM 1996]
[MOE 2063]
[MOE 2052]
[IE 2003]
[BPKIHS 2004]
[IOM-2013]
[BPKIHS-2013]
[BPKIHS -2015]
[IOM-2013]
[BPKIHS-2016]
[IOM-2015]
[IOM-2015]
[IOM-2016]
[IOM]
[IOM]
[KU 2014]
[KU 2012]