
Characters | Sarcodina | Ciliata | Mastigophora | Sporozoa |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Mode of Locomotion | Pseudopodia (Amoeboid movement) | Cilia (Coordinated, hair-like structures) | Flagella (Whip-like structures) | No locomotory organelles (Gliding or bending movements) |
Habitat | Mostly freeliving found freshwater and marine environments, few parasitic and pathogenic | Mostly freeliving found freshwater and marine environments, few parasitic and pathogenic | Both free-living and parasitic, found in various aquatic habitats | Entirely parasitic, found inside host organisms |
Reproduction | Asexual (Binary fission, sporulation), Some sexual (Syngamy) | Asexual (Binary fission), Sexual (Conjugation) | Asexual (Binary fission), Some sexual | Asexual (Sporogony), Sexual (Gamogony) |
Nucleus | Usually one nucleus, though multinucleate forms exist | Two types of nuclei (Macronucleus and Micronucleus) | Usually one or two nuclei, can be multinucleate | Single nucleus in most species |
Feeding Mechanism | Phagocytosis (Engulfing food particles) | Cytostome (Cell mouth) with food vacuoles | Absorption through general body surface or cytostome | Absorption directly from the host cells |
Examples |
|
|
|
|
Locomotory organelle | Protozoans |
|---|---|
Pseudopodia (Lobopodia) | Amoeba |
Flagella |
|
Cillia | Paramecium |
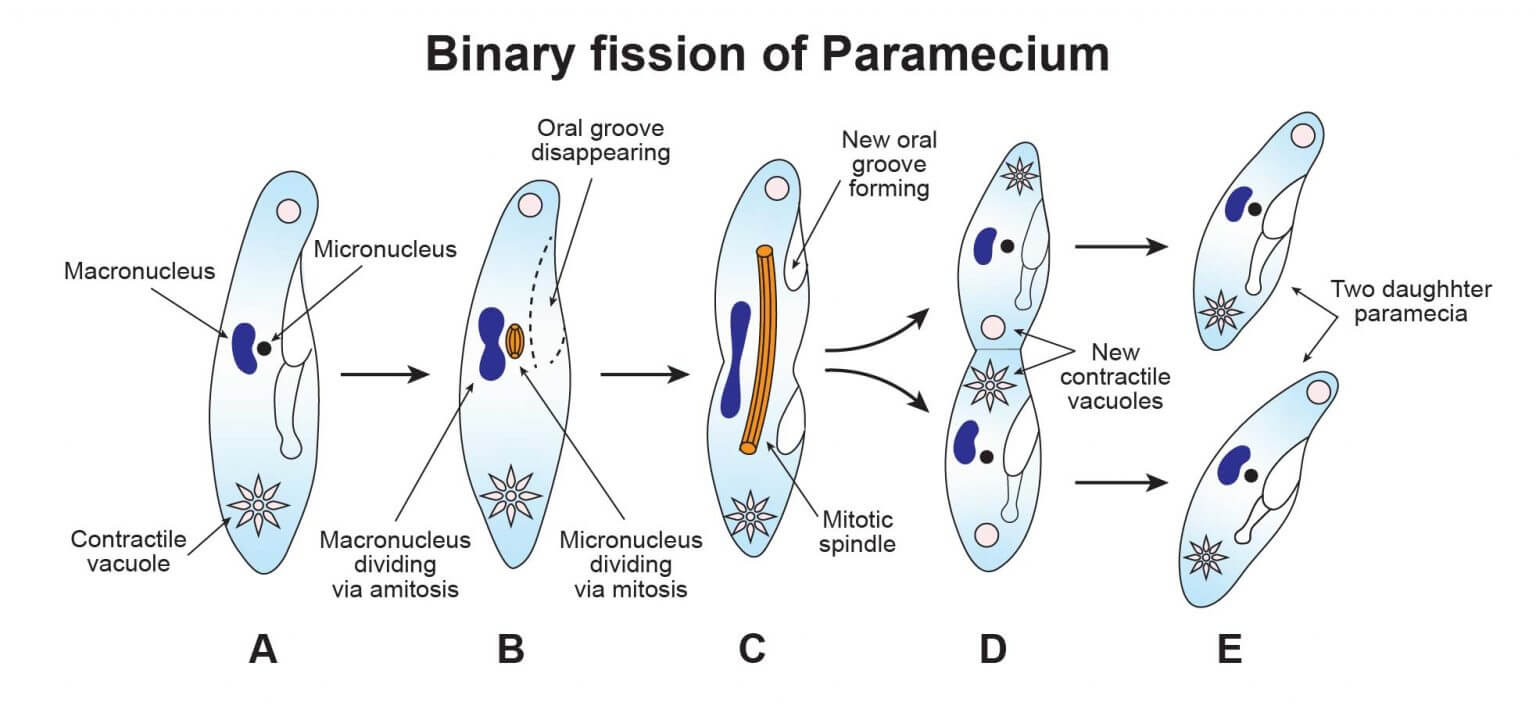
Types of Binary Fission | Protozoans |
|---|---|
Simple Binary Fission | Paramecium |
Longitudinal Binary Fission |
|
Oblique Binary Fission | Ceratium |













Form | Description |
|---|---|
Crithidial stage/Epimastigote stage | With flagella |
Leptomonas stage/Promastigote stage | With flagella |
Leishmanial stage/Amastigote stage | Without flagella |
Metacyclic stage/Trypanosomal stage | With flagella (Infective stage) |


Form | Description |
|---|---|
Trophozoite form |
|
Cystic form |
|

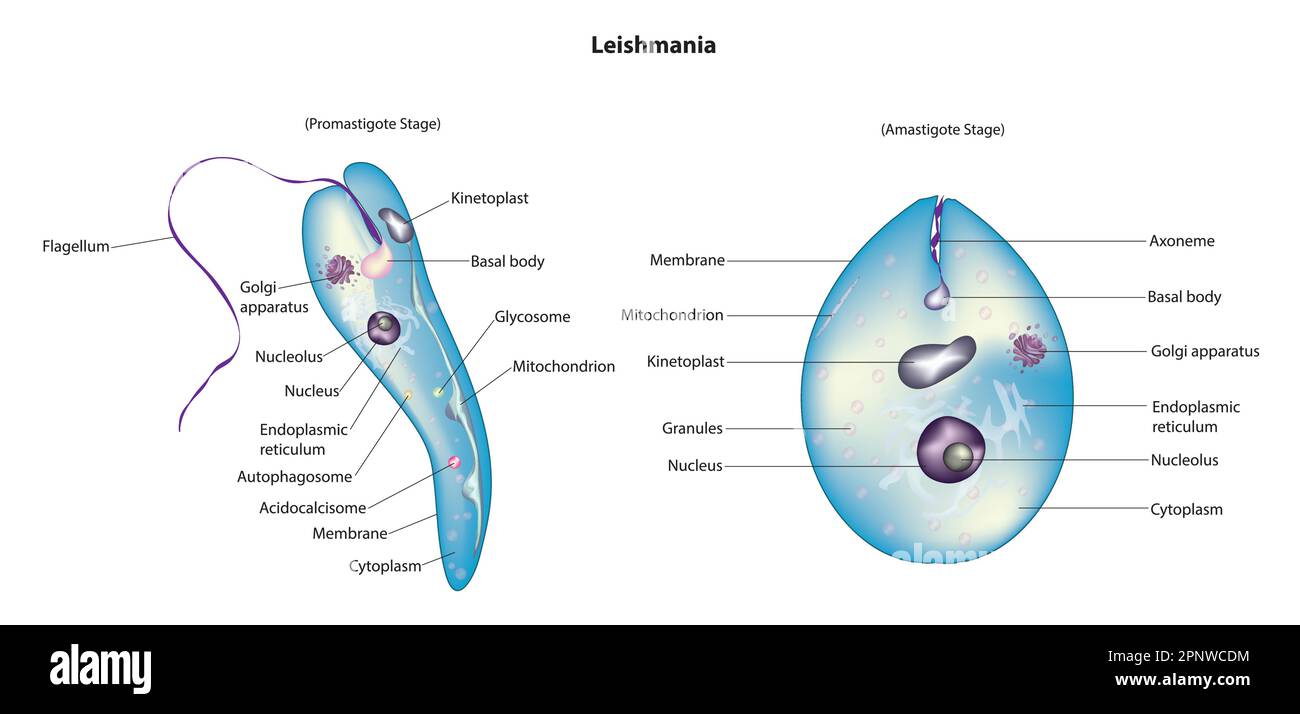

Promastigote form/Leptomonad form | Amastigote form/Leishmanial form |
|---|---|
i. Cylindrical and | i. Oval or Round and |
ii. Flagellate (Uniflagellate) | ii. Non-flagellate |
Contains Axonema and Kinetoplast. | Axonema and Kinetoplast are absent. |
Promastigote form is Infective stage as it enters the human body. | Amastigote form is Feeding stage. |
Promastigote form is found in Salivary glands and Guts of Sandfly. | Amastigote form is found in Reticulo-endothelial system of man. |
Promastigote changes into amastigote form in man. | Amastigote changes into promastigote form in Sandfly (Phlebotomus argentipus). |
S.N. | Parasite name | Disease (Types of Malaria) | Dots/ Granules | Pre-patent period | Incubation period |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
a. | Plasmodium vivax |
| Schuffner's dots/ Schuffner's granules | 8-10 days | 14 days |
b. | Plasmodium falciparum |
| Maurer's dots | 5-10 days | 12 days |
c. | Plasmodium ovale |
| Jame's dots/ Schuffner's dots | 9 days | 14 days |
d. | Plasmodium malariae |
| Ziemann's dots | 14-15 days | 28 days |

