

Category | Protoplasmic / Molecular / Acellular grade | Cellular grade | Tissue grade | Organ grade | Organ system grade |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Characteristics | All life activities occur within a single cell |
|
|
| Organs form systems specialized for specific body functions |
Examples | Protozoa and other unicellular organisms | Porifera | Cnidarians | Platyhelminthes | Nemathelminthes to Chordata |

Category | Diploblastic Animals | Triploblastic Animals |
|---|---|---|
Layers |
|
|
Formation | - | Cells of either ectoderm, or more usually, the endoderm give rise to a third germ layer, the mesoderm. |
Examples | Protozoa to Coelenterata | Platyhelminthes to Chordata |

Category | Acoelomates | Pseudocoelomates / Blastocoelomates | Eucoelomates |
|---|---|---|---|
Description | Animals without coelom or body cavity |
| Cavities bounded on all sides by mesodermal peritoneum. |
Examples |
| Nemathelminthes | Annelida to Chordata |
Subtype | Schizocoelous | Enterocoelous |
|---|---|---|
Characteristics / Formation |
|
|
Examples |
|
|
Haemocoelomates | Description Coelom filled with blood is called Haemocoel.Examples
|
[BPKIHS 2005]
[BPKIHS 2008]
[MOE 2064]
Body Plan Type | Cell aggregate body plan | Blind sac body plan | Tube within a tube body plan |
|---|---|---|---|
Characteristics |
|
|
|
Organisms | Sponges |
|
|
Characteristics | Protostomes | Deuterostomes |
|---|---|---|
Blastopore |
|
|
Coelom formation | Schizocoely | Enterocoely |
Cleavage |
|
|
Examples |
|
|
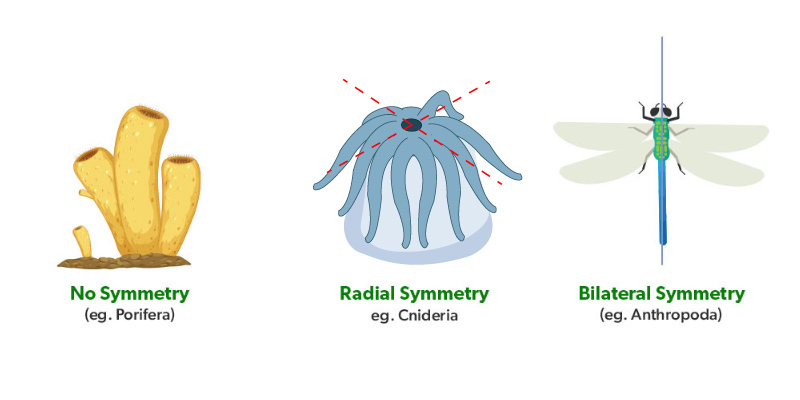
Symmetry Type | Asymmetrical | Spherical symmetry | Radial symmetry | Biradial symmetry | Bilateral symmetry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Characteristics |
|
|
|
|
|
Organisms | ▢ Protozoans: ❖ Exceptions: ◉ Spherical symmetrical:
◉ Bilateral symmetrical: Giardia lamblia ▢ Adult sponges: ❖ Exceptions: ◉ Radially symmetrical:
▢ Some molluscs:
| ▢ Protozoa:
| ▢ Sponges:
▢ Most of coelentrates: ▢ Adult Echinodermata: ❖ Larval form: Bilateral symmetry ❖ Adult: Radial symmetry |
| Flatworms to Mammals except some Molluscs and Echinodermata |
[BPKIHS 2001]
Segmentation Type | Unsegmented | Pseudosegmented | True segmentation / Metamerically segmented |
|---|---|---|---|
Characteristics | Body without a linear series of segments. |
|
|
Examples |
|
|
|



Aspect | Intracellular Digestion | Extracellular Digestion |
|---|---|---|
Definition | Digestion that occurs inside the cells with the help of lysosomal enzymes. | Digestion that occurs outside the cells in the digestive cavity with the help of secreted enzymes. |
Process |
|
|
Phyla (Examples) |
|
|
Efficiency | Less efficient as digestion is limited to individual cells. | More efficient, allowing digestion of larger and complex food materials. |
Category | Open Circulation | Closed Circulation |
|---|---|---|
Definition | Blood is not confined to blood vessels; it flows freely through body cavities (hemocoel). | Blood flows entirely within blood vessels throughout the body. |
Heart Chambers | Usually simple or absent | Can vary (2 to 4 chambers) |
Speed & Pressure | Slow and under low pressure | Faster and under high pressure |
Oxygenation | Mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood common | Usually separated unless heart is incompletely divided |
Examples |
|
|
Category | Single Circulation | Double Circulation |
|---|---|---|
Definition | Blood passes only once through the heart in a complete circuit. | Blood passes through the heart twice: once for oxygenation and once for systemic distribution. |
Heart Chambers | 2 chambers (1 atrium, 1 ventricle) | 3 or 4 chambers (2 atria, 1 or 2 ventricles) |
Oxygenation | Deoxygenated blood is oxygenated and sent directly to body. | Pulmonary and systemic circuits separate oxygenated and deoxygenated blood. |
Efficiency | Less efficient due to single pressure drop after gills | More efficient, maintains pressure in both lungs and body |
Examples |
|
|
Category | Simple Diffusion | Cutaneous Respiration | Tracheal Respiration | Branchial (Gill) Respiration | Pulmonary Respiration | Buccopharyngeal Respiration | Cloacal Respiration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Description |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Examples / Phyla |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Category | Ammonotelic | Aminotelic | Uricotelic | Ureotelic | Guanotelic |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Nitrogenous Waste | Ammonia | Amino acids | Uric acid | Urea | Guanine |
Examples |
|
|
|
|
|
[BPKIHS 2015]
[KU 2015]
Category | Sexual Reproduction | Asexual Reproduction |
|---|---|---|
Definition | Reproduction involving the fusion of male and female gametes (sperm and egg) to form a zygote. | Reproduction without the involvement of gametes; offspring arise from a single parent. |
Gametes Involved | Yes (male and female gametes) | No gametes involved |
Genetic Variation | Offspring show genetic variation (due to meiosis and recombination) | Offspring are genetically identical to parent (clones) |
Types |
|
|
Examples |
|
|
[AIPMT 2000]
| Column I (Phylum) | Column II (Level of Organization) |
|---|---|
| A. Protozoa | p. Protoplasmic |
| B. Porifera | q. Cellular |
| C. Cnidaria | r. Cell-tissue |
| D. Chordata | s. Organ-system |
| Column I (Symmetry) | Column II (Phylum) |
|---|---|
| A. Asymmetry | p. Arthropoda |
| B. Radial symmetry | q. Ctenophora |
| C. Biradial symmetry | r. Cnidaria |
| D. Bilateral symmetry | s. Porifera |
[MH-CET 2000, AFMC 2008]
[Odisha JEE 2006]
[PCS 2000, CPMT 2002, BV Pune 2003, RPMT 2005]
[CPMT 2000]
[RPMT 2000, DPMT 2001]
[JIPMER 2000, JKCMEE 2004]
[JKCMEE 2002, JKCMEE 2005]
| Column I (Phylum) | Column II (Body cavity) |
|---|---|
| A. Platyhelminthes | q. No body cavity |
| B. Nematoda | r. Pseudocoel |
| C. Annelida | s. Schizocoel |
| D. Echinodermata | p. Enterocoel |
[RPMT 2001]
[EAMCET 2000]
[RPMT 2001]
[EAMCET, Har. PMT]
[MPPMT 2000]
[Kerala PMT 2000, BHU 2001, Wardha 2011]
[DPMT 2001]
[CPMT 2000]
[MPPMT 2001]
[RPMT 2001]
[PCS 2002]
[PCS 2002]
[Odisha JEE 2002]
| Column I (Classes) | Column II (Examples) |
|---|---|
| A. Polychaeta | Nereis |
| B. Trematoda | Liver fluke |
| C. Arachnida | Scorpion |
| D. Gastropoda | Pila |
| E. Asteroidea | Starfish |
[Karnataka CET]
[JKCMEE 2006]
[EAMCET]
[AIEEE 2004]
[AIIMS 2004, 2008]
[Odisha JEE 2004]
[MPPMT 2004]
[BHU 2004, 2008; BV Pune 2001, 2008; Uttarakhand PMT; Odisha JEE 2011]
[AIIMS 2006, 2008]
[AIPMT 2006]
[Odisha JEE 2006]
[AFMC 2006; JCECE 2007]
[BV Pune 2006]
[Kerala PMT 2007]
| Column I (Organism) | Column II (Larva) |
|---|---|
| A. Petromyzon | 4. Ammocoete larva |
| B. Holothuria | 3. Auricularia larva |
| C. Ambystoma | 2. Axolotl larva |
| D. Polychaeta | 5. Trochophore larva |
| E. Cnidaria | 1. Planula larva |
[Kerala PMT 2007; EAMCET 2001]
[EAMCET 2007]
| Column I (Organism) | Column II (Common name) |
|---|---|
| A. Euplectella | 3. Venus flower basket |
| B. Physalia | 5. Portuguese man of war |
| C. Pennatula | 1. Sea pen |
| D. Enterobius | 2. Pinworm |
| E. Alytes | 4. Midwife toad |
[Kerala PMT 2007]
[AIPMT 2008]
[AIPMT 2008]
[CMC Vellore 2008]
[CMC Vellore 2008]
[OU-JEE 2008, 11]
| Column I (Phylum) | Column II (Example) |
|---|---|
| A. Protozoa | Monocystis |
| B. Aschelminthes | Wuchereria |
| C. Porifera | Cliona |
| D. Ctenophora | Beroe |
| E. Cnidaria | Pennatula |
[Kerala PMT 2008]
[Odisha JEE 2008, Pb. PMT 2008]
[AIPMT 2009]
[AMU 2009]
[Karnataka CET 2009]
[Odisha JEE 2009]
[AIPMT 2010]
[EAMCET 2010]
[EAMCET 2010]
[EAMCET 2010]
[IIPP]
[JKCMEE 2010]
[JKCMEE 2010]
[COMEDK 2010]
[AIPMT 2011]
[Kerala PMT 2011]
[JKCMEE 2011]
[JKCMEE 2011]
[JKCMEE 2011]
[MPPMT 2011]
[AIPMT 2011]
[Kerala PMT 2012]
[AIPMT 2012]
[AIPMT 2011]
[Kerala PMT 2012]
[AIPMT Mains 2012]
[Odisha JEE 2012]
[BHU 2012]
[KEET-UG 2013]
[NEET-UG 2013]
| Column I (Level of Organization) | Column II (Example) |
|---|---|
| A. Organ level | q. Fasciola |
| B. Cellular aggregate level | r. Spongilla |
| C. Tissue level | s. Obelia |
| D. Organ system level | p. Pheretima |
[Karnataka CET 2013]
[Karnataka CET 2013]
| Column I (Characteristic) | Column II (Example) |
|---|---|
| A. Incomplete digestive system | 4. Platyhelminthes |
| B. Cellular level organization | 1. Sponges |
| C. Radial symmetry | 2. Coelenterates |
| D. Pseudocoelomate | 5. Aschelminthes |
| E. Metamerism | 3. Annelids |
[Kerala PMT 2014]
[MH-CET 2014]
[JKCMEE 2015]
[Kerala PMT 2015]