1.
[12072]
➤
2.
[2071, 2070, 2053, 2075]
➤
3.
➤
4.
[81062, 0561]
➤
5.
➤
6.
[41058]
➤
7.
[51057]
➤
8.
[61056]
➤
9.
[074, 077]
➤
10.
➤
11.
[207]
➤
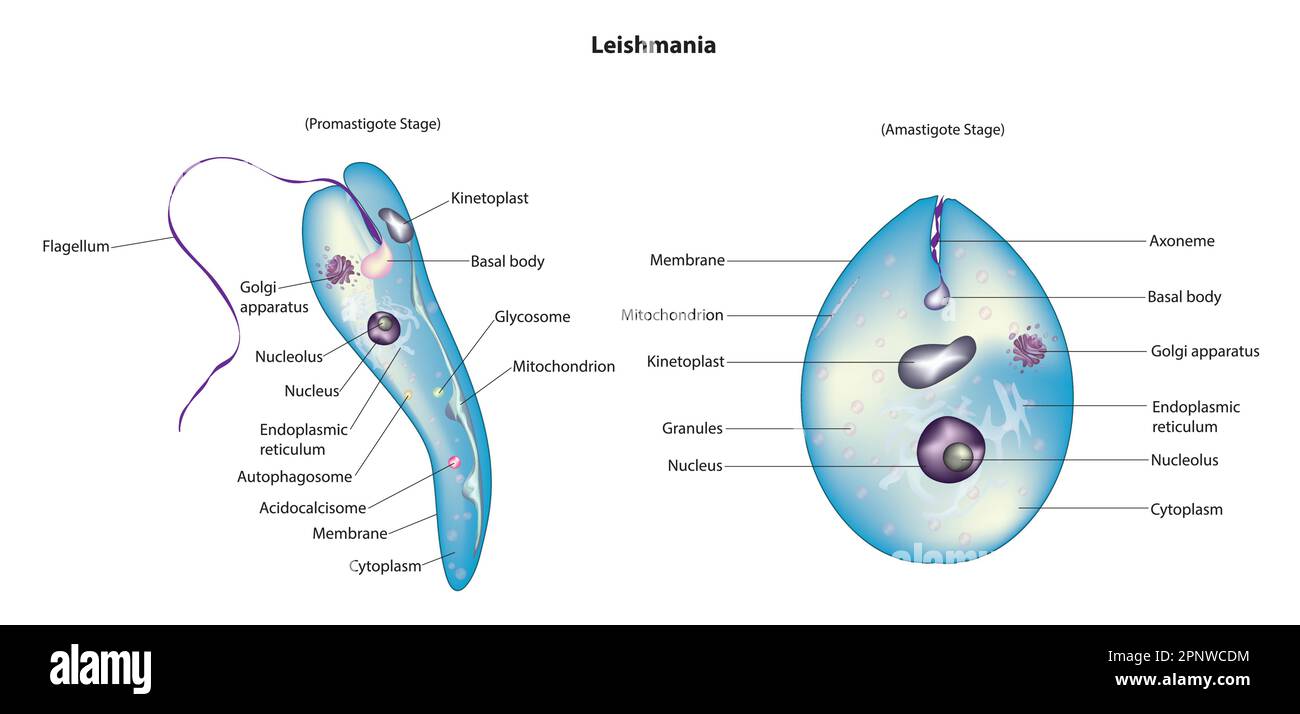

Promastigote form/Leptomonad form | Amastigote form/Leishmanial form |
|---|---|
i. Cylindrical and | i. Oval or Round and |
ii. Flagellate (Uniflagellate) | ii. Non-flagellate |
Contains Axonema and Kinetoplast. | Axonema and Kinetoplast are absent. |
Promastigote form is Infective stage as it enters the human body. | Amastigote form is Feeding stage. |
Promastigote form is found in Salivary glands and Guts of Sandfly. | Amastigote form is found in Reticulo-endothelial system of man. |
Promastigote changes into amastigote form in man. | Amastigote changes into promastigote form in Sandfly (Phlebotomus argentipus). |